Forests are valuable assets of our planet, they serve as the lungs of the Earth. When it comes to the contribution of forests, Indonesian forests play a major role, offering not only breathtaking landscapes and biodiversity but also invaluable benefits to the global environment.
Indonesia’s forests rank 8th among the world’s top 10 largest forests. According to data from the Central Statistics Agency (BPS), Indonesian forests cover an area of 131 million hectares, harboring rich and diverse biodiversity. The Nature Conservancy reports that Indonesian forests are home to 50,000 plant species, 515 mammal species, and 3,000 freshwater fish species. Indonesia’s forests house 10% of the world’s plant species, 12% of mammal species, and 17% of bird species. Additionally, the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) states that more than 10% of the world’s plant, mammal, and bird species originate from Indonesia.

According to the second report of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Indonesian forests absorbed approximately 331 million tons of CO2 in 2020. This is attributed to the carbon potential stored in the vegetation, soil, and biomass of Indonesian forests. However, despite their rich flora and fauna, Indonesia’s forests are currently facing threats from irresponsible parties engaged in illegal deforestation. Illegal deforestation involves significant and permanent forest loss through unauthorized logging and burning, bypassing applicable legal regulations. Illegal deforestation activities are often driven by financial motives, aiming for quick profits without considering the long-term impacts on the environment and communities. From 2002 to 2020, Indonesia lost more than 24 million hectares of forest.
The Indonesian government, through the Ministry of Environment and Forestry (KLHK) of the Republic of Indonesia, continues to make efforts to address the issue of illegal deforestation through the following measures:
- Law Enforcement and Supervision KLHK has increased law enforcement efforts against illegal deforestation through collaborations with the police and relevant agencies to combat illegal logging. KLHK has tightened the licensing process and supervision of forest activities such as logging and other forest uses.
- Forest Restoration Programs KLHK has launched forest restoration and rehabilitation programs to restore deforested areas. KLHK also develops reforestation programs through sustainable industrial timber plantations.
- Forest Information System KLHK has strengthened forest information and monitoring systems using satellite and drone technologies for real-time monitoring.
- Awareness and Education KLHK conducts public awareness campaigns and education about the importance of preserving forest sustainability.
- International Cooperation KLHK collaborates with other countries, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations to share knowledge, technology, and resources in combating deforestation.
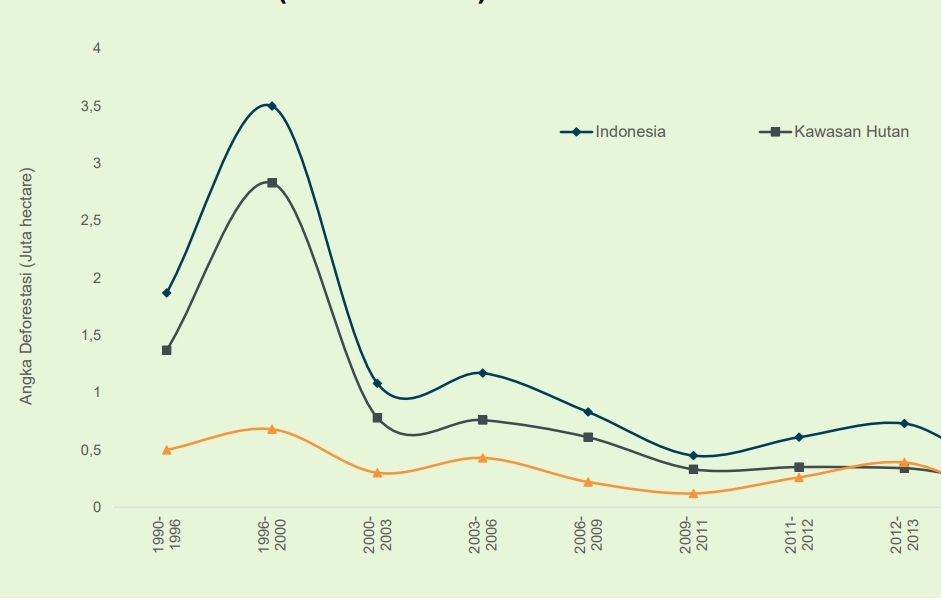
These efforts have been effective, as evidenced by the significant decreasing trend in deforestation activities in Indonesia over the past 20 years. KLHK continues to target further reduction in deforestation rates.
Managing forest resources in the industry requires certification and validation from international and national institutions. Two certification systems related to sustainable forest management and deforestation mitigation are PEFC (Program for the Endorsement of Forest Certification) and SVLK (Timber Legality Verification System)
PEFC (Program for the Endorsement of Forest Certification) is an international program that provides certification for sustainable forest management. PEFC establishes standards and criteria that forest managers must meet to ensure that logging and forest management practices are economically, ecologically, and socially sustainable. PEFC recognizes and supports sustainable practices in forest management, including efforts to combat illegal deforestation and protect biodiversity

SVLK (Timber Legality Verification System) is a verification system established by the Indonesian government to ensure the legality of timber obtained from Indonesian forests. SVLK ensures that the harvested and traded timber is sourced legally and complies with the required permits and applicable forest management regulations.

Overall, PEFC and SVLK efforts aim to promote sustainable forest management and combat deforestation. Through PEFC certification and SVLK implementation, traded timber can be ensured to come from legal, sustainable sources, preventing uncontrolled environmental damage. This is crucial in maintaining forest sustainability and reducing the negative impacts of deforestation on ecosystems, biodiversity, and communities dependent on forests.
Asia Pulp and Paper Sinarmas has already implemented PEFC and SVLK certifications in its business schemes. One of Asia Pulp and Paper’s product for the food packaging segment is Foopak. All Foopak products are certified by PEFC and SVLK, guaranteeing that the raw materials are verified through government-established legality regulations.
According to the Asia Pulp and Paper Sustainability Report 2022, Asia Pulp and Paper has maintained 94% of its concession areas for PEFC certification, with the remaining 6% under the mandatory SVLK scheme. Asia Pulp and Paper remain committed to ensuring that 100% of plantation wood is managed sustainably and responsibly. Therefore, it is essential for the government, industry, and society to synergize in order to preserve the sustainability of Indonesian forests. “Let us together protect the forests, for safeguarding the forests is an act of courage and wisdom, taking responsibility for the natural heritage to realize a sustainable life for us and future generations.”

